Product Management Process Introduction
Trying to wrap your head around the product management process? You’re not alone.
Product management is becoming an increasingly popular role across both startups and enterprise companies, but it’s still difficult to define. That’s because it doesn’t fit any of the traditional roles you may already be familiar with, such as engineering, business strategy, design, or marketing.
Instead, product management draws on all these fields, forming a critical new discipline. It has become increasingly important among startups and enterprise companies alike.
Introduce best practice into your product management process
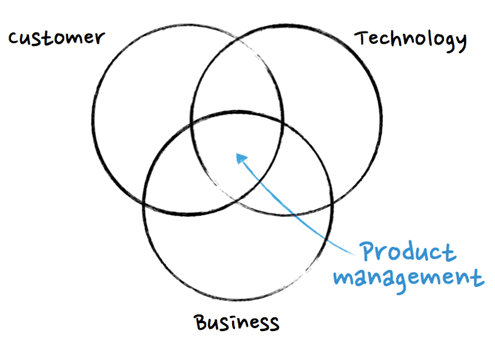
What is Product Management?
Product management is an interdisciplinary role that reaches across teams to plan, design, and continuously bring better products to market.
The role evolved out of a set of responsibilities that traditionally fell to lead developers and engineers: scoping out user problems and making critical product decisions.
Since then, it’s become clear that successful product leadership – and shipping successful products – goes beyond the scope of a dev team. It’s a separate function that requires business acumen, a deep understanding of UX design and product knowledge.
Product managers are responsible for setting a product vision, and defining a product strategy. They are also responsible for developing a roadmap that meets both company goals and user needs. (Here’s an excellent introduction to the role of a product manager.)
The primary question they’re out to answer is this:
How do we bring the best possible product to market and grow our business?
What are Product Management Processes?
Idea Management
In this phase of the product management process, new suggestions, ideas and feature requests are captured as part of the product backlog. These serve as good sources of inspiration for your product’s evolution, and the good ideas should be locked down and developed further.
Product Specifications
In the spec phase of the product management process, ideas and feature requests from the product backlog are fleshed out into more detail. This is in order to better understand the impact and effort expected for each.
Roadmapping
In this phase, your entire product strategy and vision is taken into account, and focus is put on the initiatives that line up with the big vision of the product. A roadmap is a communication tool that helps communicate where you are, where you are heading and how you expect to get there.
Prioritization
In this phase, a more detailed look is taken at your backlog and your roadmap, with the goal of setting priorities based on a variety of inputs. The process involves deciding what should be built when, based on what will bring most value to the user and the product.
Delivery
In this phase of the product management process, the product manager works closely with the engineering, marketing, support, and other teams to make sure features are delivered to a high quality and product specification.
Analytics & Experiments
In this phase, experiments are run and analytics are tracked in order to continually test and improve your product and understand what’s truly of value to your users.
Customer Feedback
Throughout the cycle, customer feedback plays a key role in validating and improving on proposed features and products. It offers direct insight and suggestions that help you to understand how you are doing at solving the problems you’re already trying to address. It also helps in discovering new problems you weren’t aware of.