Opportunity Solution Tree
What is an Opportunity Solution Tree?
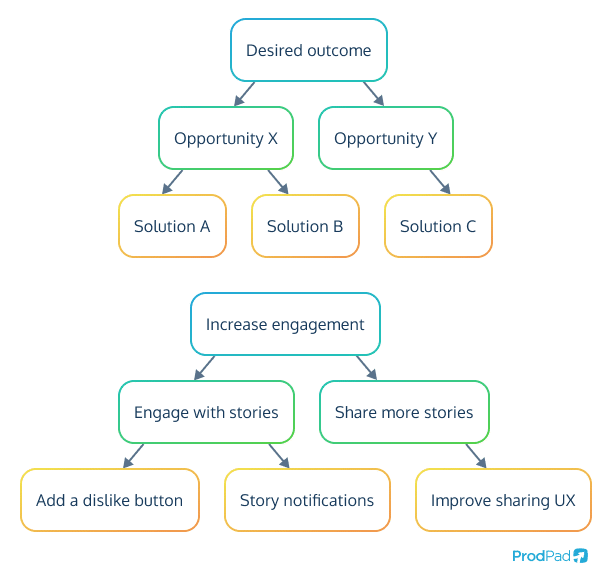
The Opportunity Solution Tree (OST) is a visual framework used to systematically explore desired business outcomes, potential opportunities, and their corresponding solutions. It helps to identify the root cause of a problem, analyze possible solutions, and organize a roadmap for implementation.
Its purpose is to help product managers and teams identify and prioritize potential solutions that best address customer needs and business goals.
There are three levels to the Opportunity Solution Tree. They are:
- The Desired Outcome: What you want to achieve.
- Opportunities: One direction that could help achieve the desired outcome.
- Solutions: The specific things you will do to implement the opportunity
How do you structure an OST?
The structure of an Opportunity Solution Tree is based on three branching levels. The first level is made up of desired outcomes. These are the business objectives or goals that the product aims to achieve. These outcomes guide the entire discovery process.
Branching out from the outcomes are the opportunities, which represent potential areas where the product could create value for customers or the business. These opportunities are often identified through brainstorming sessions and the study of customer feedback.
Each opportunity then leads to a set of potential solutions, which are various ideas or features that could address the identified opportunity. Solutions can range from small tweaks to the product to entirely new features or products.
To validate and test the potential solutions, product managers design and construct experiments. These experiments help uncover user feedback, validate assumptions, and gather data that can inform the decision-making process.

What is the origin of the OST?
The Opportunity Solution Tree was created in 2016 by Teresa Torres, a renowned product discovery coach, to streamline the product discovery process. Torres recognized the need for a visual representation that could help product teams navigate the complexity of making product decisions and reaching desired outcomes.
“The Opportunity Solution Tree visualizes what you are learning in discovery and the decisions you are making along the way.”
– Teresa Torres
With the OST, Torres aimed to make implicit assumptions explicit by providing a structured framework for product teams. By mapping out the various branches and opportunities, the OST helps teams identify and prioritize potential solutions to achieve the desired outcomes.
How does the Opportunity Solution Tree work?
The key components of an OST are outcomes, opportunities, and solutions. An outcome is a specific business objective or goal, while opportunities are the potential ways to achieve these outcomes. Solutions, on the other hand, are the specific actions or features that can address the identified opportunities.
The process of creating an OST involves mapping out these components in a visualized tree format. The tree starts with the desired outcome at the top level, with branches representing different opportunities to achieve that outcome. Each branch can then further branch out into different potential solutions related to the respective opportunity.
How do you build an OST?
To build your Opportunity Solution Tree, you’ll need to take the following steps:
- Identify problems: Begin by defining the problem or challenge you want to address. Pick a definable single metric.
- Brainstorm opportunities: Conduct brainstorming sessions to generate a wide range of potential opportunities related to the identified problem. Encourage creativity and free thinking during this stage.
- Organize opportunities: Categorize and group similar opportunities together. This helps in creating a more organized and manageable structure for further analysis.
- Evaluate feasibility: Assess the feasibility and viability of each opportunity. Consider factors such as resources required, potential return on investment, and alignment with the organization’s goals.
- Identify solutions: For each opportunity, explore and map out potential solutions. Determine which solution aligns best with the opportunity and its feasibility.
- Create an action plan: Develop a roadmap for implementation. Outline the necessary steps, responsibilities, and timelines for executing the chosen solution effectively.
- Test and iterate: Implement the solution on a small scale to test its effectiveness. Gather feedback and data to make improvements before full-scale implementation.
The visualization of the current state of play and plan of action in OSTs helps teams gain a clear understanding of the connections between outcomes, opportunities, and solutions. It enables teams to see how their work aligns with the overall business goals and allows for effective communication and collaboration.
It also aids in validating and prioritizing work. By having a clear visual representation, teams can assess and evaluate which opportunities and solutions are most likely to have the desired impact. They can validate their assumptions and hypotheses, and make data-informed decisions on what to prioritize in their product development process.
Benefits of using an OST
An Opportunity Solution Tree (OST) offers several benefits when used in the product development process:
Efficient resource management
One of the primary advantages of employing an Opportunity Solution Tree is the efficient allocation of resources. By evaluating potential solutions beforehand, businesses can prioritize and invest resources in the most promising opportunities.
This approach minimizes resource wastage on less viable options. This ensures that time, money, and efforts are channeled into initiatives with the highest likelihood of success. As a result, you can optimize your resource utilization, which is especially valuable if you are part of a startup or a small business with limited resources.
Helps with prioritization
OSTs help product teams to identify key opportunities by layering customer needs and pain points. By understanding these areas of opportunity, teams can prioritize the solutions that will have the greatest impact on improving customer satisfaction and achieving business objectives.
This helps product managers to make strategic product decisions that are aligned with their product vision as well as the needs and preferences of their target customers.
Streamlined decision-making
Traditional problem-solving processes can sometimes lead to analysis paralysis, with teams overwhelmed by the complexity of the problem and an abundance of potential solutions.
The visual nature of the OST simplifies decision-making by presenting all options in a structured and easily comprehensible manner. This enables stakeholders to make faster, more informed choices, reducing delays and keeping projects on track.
Increased success rate
The systematic analysis and testing of potential solutions provided by the OST can contribute to a higher success rate in implementation. By thoroughly evaluating the feasibility and potential impact of each opportunity, you can identify and address potential roadblocks and risks early in the process.
The iterative approach of testing and refining solutions before full-scale implementation minimizes the chances of failure and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Adaptability and scalability
The flexibility of the OST makes it suitable for projects of various scales and complexities. You can tailor it to suit the specific needs and goals of the organization, whether you use it for individual initiatives or broader company-wide strategies.
This adaptability allows businesses to apply the framework consistently across departments and projects, promoting a unified problem-solving approach throughout the organization.
Employee empowerment
Involving various internal stakeholders in the process fosters a communal sense of ownership and empowerment. When team members actively participate in generating ideas, evaluating opportunities, and developing solutions, they become more invested in the success of the project.
Increasing your team members’ sense of responsibility and autonomy can significantly boost their motivation, teamwork, and overall productivity.
Enhanced creativity and innovation
The Opportunity Solution Tree encourages innovation. By exploring a wide range of potential opportunities and solutions, teams are inspired to think creatively and explore unconventional approaches to problem-solving.
Emphasizing innovation can give companies a competitive edge in the market, as they are better equipped to adapt to changing circumstances and seize emerging opportunities.
Downsides to using an OST
While an Opportunity Solution Tree offers numerous advantages in the product discovery process, there are also some downsides that product teams may encounter when implementing this approach.
Time-consuming
Constructing a comprehensive OST can be a time-consuming process, particularly when dealing with complex problems or projects involving multiple stakeholders. The need for extensive data gathering, brainstorming sessions, and analysis can slow down decision-making, making it unsuitable for urgent or time-critical situations.
Possible subjectivity in evaluation
While the OST provides a structured framework for analysis, there is still room for subjectivity in evaluating opportunities and solutions. Different stakeholders may have varying perspectives on the potential impact, feasibility, and risks associated with each option. As a result, the conclusions drawn from an OST may not always be entirely objective.
Another limitation is the potential bias towards known solutions. If the product managers on the team have preconceived ideas or preferences for certain solutions, it can limit the exploration of new and innovative possibilities. This can restrict the discovery process and hinder the team from identifying more impactful opportunities.
Limited by input quality
The effectiveness of an Opportunity Solution Tree heavily depends on the quality of the data and information used as inputs. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed analysis and decision-making. Ensuring that the right data is available and accurate is crucial to deriving meaningful insights from the OST.
The quality is highly reliant on how well the problem is initially defined. If the problem statement is unclear or too narrow, it may limit the scope of potential opportunities identified, impacting the effectiveness of the solution development process.
Resistance to change
Introducing a new problem-solving approach like the OST may face resistance from some team members, especially those who are accustomed to traditional methods. Overcoming resistance to change and ensuring buy-in from all stakeholders can be a challenge, potentially hindering successfully implementing it.