AARRR (Pirate Metrics)
What is AARRR?
AARRR, playfully referred to as the “Pirate Metrics,” is a useful framework that guides Product managers through the critical stages of user behavior and product performance.
Originating from the mind of entrepreneur and angel investor Dave McClure, the acronym stands for Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, and Revenue.
AARRR metrics provide a structured approach to evaluating a product’s lifecycle from a customer’s first interaction to their ultimate contribution to revenue, making them a core part of modern product management frameworks.
While AARRR is not a prioritization tool in itself, it is often used alongside prioritization frameworks to ensure teams are focusing on the right problems at the right stage of growth.
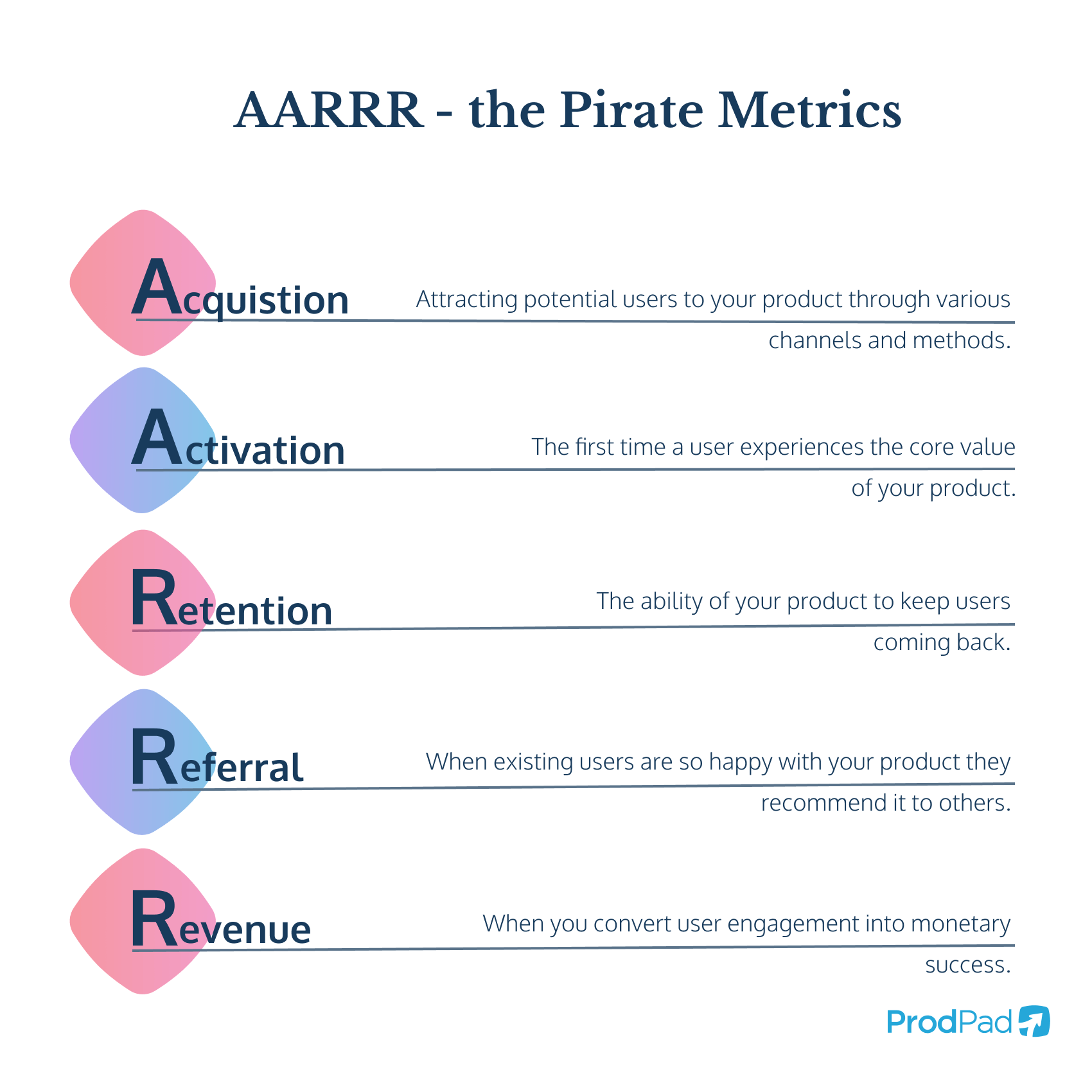
The AARRR framework breaks down the customer journey into five essential stages:
- Acquisition: The process of attracting potential users to your product through various channels and methods.
- Activation: The moment a user experiences the core value of your product for the first time.
- Retention: The ability of your product to keep users coming back after their first experience.
- Referral: When existing users are so satisfied with your product that they recommend it to others, driving organic growth.
- Revenue: The ultimate goal of converting user engagement into monetary success.
By focusing on these five groups and their associated metrics, you can pinpoint strengths, uncover areas for improvement, and align your efforts with the product’s growth strategy.
Each of these stages is interconnected, forming a continuous loop that feeds back into itself. For example, Retention (satisfied users) is often one of the clearest signals of product-market fit, while Referrals are satisfied users who become advocates can lead to Acquisition (new users), starting the cycle anew.
The AARRR framework provides a structured approach to navigating this cycle, enabling you to identify opportunities for optimization and growth at every stage of the user journey. It helps to navigate the complexities of user behavior and product performance metrics.
Acquisition
Acquisition is the very first step in the user’s journey, where the primary focus is on attracting potential users to your product. This stage is about casting a wide net through various channels such as social media, search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and content marketing.
The goal here isn’t just to generate traffic. You need to attract the right kind of users who are likely to find value in your product. Effective acquisition strategies are tailored to the specific demographics, interests, and behaviors of your target audience, ensuring that the first touchpoint is relevant and engaging.
For a growth product manager, acquisition metrics help determine which channels bring in users who are most likely to activate, retain, and eventually convert to revenue.
Examples of acquisition metrics:
- Website traffic: Total visits, unique visitors, page views, and the source of the traffic (organic, paid, referral, etc.).
- Conversion rate: The percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as signing up for a trial or subscribing to a newsletter.
- Cost per acquisition (CPA): The total cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and advertising expenses.
- Lead generation: The number of leads generated through various channels, indicating the potential for new user acquisition.
Examples of acquisition strategies:
- Content marketing: Developing high-quality, relevant content that addresses potential users’ pain points or interests, improving SEO, and attracting organic traffic.
- Social media campaigns: Leveraging platforms like LinkedIn or X (Twitter) to engage with their communities, sharing insights, and promoting product features.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with educational institutions or coding bootcamps by offering your software as a learning tool, thereby introducing your product to new users.
- Referral programs: Implementing a system where current users can invite fellow developers, offering them benefits such as extended trial periods or premium feature access.
Activation
Activation is that critical moment when a user first realizes the true value of your product. This stage is about making a strong first impression, one that turns a casual visitor into an engaged user.
Activation is often measured by specific actions taken by the user, such as signing up for a trial, completing a profile setup, or successfully performing a key task within the product. The activation phase is crucial for demonstrating the immediate value of your product and encouraging people to come back. This is often closely tied to effective onboarding, ensuring users understand how to get started and achieve early success.
Clear activation metrics such as completing a setup flow or reaching a “first win”, help teams understand whether users are truly engaging or dropping off early.
Examples of activation metrics:
- Activation rate: The percentage of new users who achieve a predefined “activation” event, such as completing an onboarding process or creating their first project.
- Time to activation: The average time it takes for a new user to reach the activation event after signing up.
- User engagement: Key actions taken by new users within a specific timeframe, indicating early engagement with the product.
- Onboarding completion rate: The percentage of users who complete the onboarding process out of those who started it.
Examples of activation strategies:
- Onboarding tutorials: Creating interactive tutorials or walkthroughs that guide new users through the software’s key features, ensuring they understand the value proposition early on.
- Free trials or freemium models: Offering new users a taste of your product’s full capabilities without an immediate financial commitment, encouraging them to start using the software actively.
- Quick wins: Designing the product experience to deliver immediate value, such as a code analysis tool that provides actionable feedback on the user’s first upload.
- Community engagement: Encouraging new users to join a community forum or Slack channel where they can learn from and engage with other users, thereby increasing their commitment to the product.
Retention
Retention focuses on keeping users engaged with your product over time. This metric is vital for long-term success, as it’s a lot cheaper to keep existing users than to acquire new ones.
Retention strategies may include optimizing the user experience, providing exceptional customer support, releasing regular updates, and engaging users with personalized communication. High retention rates are a strong indicator of product-market fit and user satisfaction.
Retention insights often surface through ongoing customer feedback, usage patterns, and cohort analysis, helping teams understand what keeps users coming back.
Examples of retention metrics:
- Daily/monthly active users (DAU/MAU): The number of unique users who engage with the product daily or monthly, providing insight into regular usage.
- Retention rate: The percentage of users who return to the product within a certain time period after their first use.
- Churn rate: The percentage of users who stop using the product over a specific period.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total revenue expected from a user over the duration of their relationship with the product.
Examples of retention strategies
- Regular updates and new features: Continuously improving the software and introducing new features based on user feedback, keeping the product relevant and valuable.
- Customer support: Offering robust customer support, including detailed documentation, responsive help desks, and community forums to assist users with any issues.
- User feedback loops: Implementing mechanisms for collecting and acting on user feedback, showing users that their input directly influences the product roadmap.
- Engagement emails: Sending targeted, personalized emails highlighting new features, tips, and best practices to keep users engaged and informed.
Referral
Referral occurs when your existing users become advocates for your product, recommending it to others. This stage leverages word-of-mouth marketing, one of the most effective and cost-efficient ways to acquire new users.
Encouraging referrals can involve implementing referral programs, incentives, and making it easy for users to share your product with their network. A strong referral rate indicates that your users not only see value in your product but are also willing to stake their reputation on it. This behavior often emerges naturally when teams invest in long-term value, strong retention, and a clear product strategy focused on solving real user problems.
Examples of referral metrics:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): A measure of how likely users are to recommend the product to others, typically on a scale from -100 to 100.
- Referral rate: The percentage of users who refer new users to the product.
- Viral coefficient: The number of new users each existing user generates, indicating the effectiveness of referral mechanisms.
- Share of voice: Online mentions of the product compared to competitors, indicating the level of word-of-mouth and referrals.
Examples of referral strategies:
- User testimonials and case studies: Showcasing success stories and testimonials from satisfied users, encouraging them to share their positive experiences with peers.
- Affiliate marketing programs: Partnering with influencers or prominent figures in the software development field who can authentically promote your product to their audience.
- Shareable content: Creating valuable, shareable content such as insightful blog posts, webinars, or open-source projects that users are motivated to share within their networks.
- Incentivized referral programs: Offering existing users perks, such as additional storage, premium features, or discounts, for referring new users to the software.
Revenue
Revenue is the ultimate goal of the AARRR framework, where all your previous efforts converge to drive monetary success. This stage is about converting engaged users into paying customers, whether through direct sales, subscriptions, in-app purchases, or other monetization strategies.
Revenue metrics help evaluate the financial health and sustainability of your product, guiding further investment and growth strategies.
Examples of revenue metrics:
- Average revenue per user (ARPU): The average revenue generated per user, which can be tracked monthly (MRR) or annually (ARR) for subscription-based models.
- Conversion rate to paid: The percentage of users who convert from a free or trial version to a paid subscription.
- Revenue growth rate: The rate at which revenue is growing over specific periods, indicating the financial health of the product.
- Lifetime value to customer acquisition cost ratio (LTV:CAC): The ratio of the lifetime value of a customer to the cost of acquiring that customer, indicating the efficiency of revenue generation efforts.
Examples of revenue strategies:
- Subscription models: Implementing tiered subscription plans that cater to different user needs and budgets, encouraging upgrades as users’ requirements grow.
- In-app purchases: Offering in-app purchases for premium features or content, allowing users to customize their software experience to their needs.
- Licensing agreements: For enterprise clients, providing customized licensing agreements that meet the specific needs of large organizations or teams.
- Cross-selling and upselling: Identifying opportunities to offer existing users additional products or services that complement their current usage, enhancing their experience and increasing revenue.
Ensure you’re tracking the most important metrics, including everything that you’ll need to implement AARRR effectively, in our eBook, The Complete List of Product Management KPIs.

Why are AARRR metrics important?
AARRR metrics are crucial because they provide a clear and actionable framework for measuring product success. They enable teams to:
- Understand user behavior and preferences.
- Identify the most effective channels for user acquisition.
- Measure the impact of improvements and changes to the product.
- Drive strategic decisions based on data rather than intuition.
In essence, AARRR metrics offer a roadmap for product optimization, focusing on areas that directly contribute to user satisfaction and financial viability. These metrics are not just numbers on a dashboard; they are insights that can guide your strategic decision-making, product development, and market positioning.
Let’s explore some of the main reasons why AARRR metrics can be so instrumental for Product Managers:
Strategic decision-making
AARRR metrics empower you with data-driven insights, enabling you to make informed decisions that align with the product’s and the company’s overarching goals. By focusing on the Pirate Metrics, you can prioritize your teams’ efforts in a way that contributes most significantly to both growth and sustainability.
For instance, if your data indicates low user retention despite high acquisition rates, you might decide to focus on improving user engagement and satisfaction before investing more heavily in acquisition strategies.
Product development and iteration
Each stage of the AARRR framework requires gathering specific feedback on how users interact with your product, highlighting areas where improvements can have the most impact. Activation and retention metrics, for example, can inform product teams about features that users find most valuable or areas where the user experience may be lacking.
This feedback loop is crucial for iterative product development, ensuring that each update or new feature addresses real user needs and contributes to a more compelling value proposition.
Efficient resource allocation
By identifying which stages of the user journey require the most attention, AARRR metrics help you to allocate your resources more efficiently. Instead of spreading efforts thinly across various initiatives, your teams can concentrate on strategies that promise the highest return on investment (ROI).
For example, if your referral rates are low, investing in a referral program with incentives for users might be a strategic move to leverage satisfied users’ networks, driving acquisition at a lower cost.
Enhanced user understanding
AARRR metrics shed light on the user journey from their initial interaction with your product to the point where they become paying customers and advocates. This comprehensive view can help you understand the motivations, preferences, and pain points of your users.
Armed with this knowledge, your teams can tailor marketing messages, improve existing product features, and create a user experience that meets or exceeds expectations.
Long-term growth and scalability
Focusing on AARRR metrics fosters a culture of continuous improvement and growth. By systematically addressing each stage of the framework, product teams can enhance user satisfaction, reduce churn, increase revenue, and ultimately achieve a scalable business model.
Moreover, the insights gained from AARRR metrics can inform strategic planning, helping to identify new market opportunities, refine the product roadmap, and stay ahead of the competition.
How do you use the AARRR pirate metrics?
Using the AARRR metrics effectively requires a cycle of measurement, analysis, and adaptation to drive sustainable growth and user engagement.
Here’s a step-by-step process for using AARRR metrics to drive product success:
1 – Establish clear objectives for each metric
The first step is to define what success looks like for each stage of the AARRR framework by setting clear, measurable goals.
These goals should be specific, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a goal for activation might be “Increase the percentage of users who complete the onboarding process within their first week from 40% to 60% within three months.”
2 – Implement tracking and analytics tools
To measure progress toward your objectives, you need to track user interactions and transactions accurately. Implement analytics tools and tracking mechanisms across your product and marketing channels.
This might involve integrating web analytics platforms such as Google Analytics with your product for acquisition and activation data and using specialized tools like Mixpanel or Amplitude for deeper insights into user behavior and Retention.
3 – Analyze data to identify patterns and opportunities
With data collection in place, regularly analyze your metrics to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Look for correlations between the different stages of the AARRR funnel.
For example, analyze which acquisition channels bring in users with the highest Lifetime Value (LTV) or which features activated users engage with the most. This analysis will reveal what’s working well and where there are opportunities to optimize.
4 – Take action to optimize each stage
Based on your analysis, implement targeted strategies to optimize each stage of the AARRR framework.
- For Acquisition, you might explore new channels or refine your messaging.
- To improve Activation, consider streamlining your onboarding process or highlighting key features more effectively.
- For Retention, you may introduce user feedback loops, enhance customer support, or release regular updates to keep users engaged.
- To boost Referral rates, create referral programs or incentives that encourage users to share your product.
- Finally, for Revenue, experiment with different pricing strategies or upsell opportunities to increase user spend.
5 – Iterate and refine based on feedback and results
The AARRR framework is not a one-time process but a cycle of continuous improvement. As you take action to optimize each metric, monitor the impact of your changes and gather user feedback.
Use this information to refine your strategies, making iterative improvements over time. This process of measurement, analysis, action, and refinement should become an integral part of your Product Management practices, helping to drive your product’s ongoing growth and improvement.
6 – Foster a data-driven culture
To maximize the effectiveness of AARRR metrics, cultivate a data-driven culture within your team and organization. Encourage open sharing of data insights, celebrate wins in improving metrics, and foster collaboration across departments to address challenges in the AARRR framework.
A shared commitment to data-driven decision-making will empower your team to make informed, impactful choices that drive product success.
By following these steps, you’ll already have gone a long way toward understanding and optimizing your user journey. From initial user acquisition to generating consistent revenue, each stage of the AARRR framework offers opportunities for improvement and growth.
With a strategic approach and a commitment to continuous iteration, the AARRR metrics can guide your teams to achieve their goals and build successful, user-centered products.
Examples of AARRR in practice
To give you an idea of how the AARRR metrics can be applied in practice, let’s explore examples across various stages of the user journey, highlighting how different well-known companies have implemented these metrics to drive their growth and product success. These real-world examples demonstrate how AARRR metrics can be strategically applied across different industries to drive growth, enhance user experience, and increase revenue.
Each of these companies’ approaches reflects their unique product offerings and market positioning, highlighting how versatile and effective the AARRR framework can be in guiding Product Management strategies, as well as the importance of tailoring your strategy to suit both your product and market.
Acquisition: Dropbox
Dropbox excelled in user acquisition by leveraging a simple yet effective referral program that offered additional storage space for both the referrer and the referee. This strategy capitalized on existing users to drive new user acquisition, significantly reducing the cost per acquisition, and rapidly expanding their user base.
Dropbox also used SEO and content marketing effectively, positioning itself as an early leader in cloud storage solutions and attracting organic traffic.
Activation: Slack
Slack’s activation strategy focused on demonstrating value to users from the first interaction. By encouraging new users to create or join a workspace and start messaging immediately, Slack ensured that users quickly recognized how useful it was as a team communication tool.
The platform’s intuitive design and interactive onboarding process, which includes guided tours and tips, helped new users understand and utilize key features, boosting activation rates.
Retention: Spotify
Spotify has successfully maintained high retention rates through iterating on their personalized experiences, such as the Discover Weekly and Year in Review playlists. By leveraging data analytics to understand user preferences and listening habits, Spotify delivers customized content that keeps users engaged over time.
Spotify’s regular introduction of new features and content, along with its social sharing capabilities, encourages users to return and explore new music regularly.
Referral: Airbnb
Airbnb’s referral program has been a key driver of its growth, offering credits to both the referrer and the new guest or host who signs up. This strategy not only incentivized existing users to share Airbnb with friends and family but also ensured that new users had a positive first experience by providing a discount on their first booking.
The simplicity and mutual benefits of the referral program contributed significantly to Airbnb’s viral growth and market penetration.
Revenue: Salesforce
Salesforce employs a tiered subscription model to drive revenue, offering different levels of features and customization options to cater to a wide range of business needs. This strategy encourages users to start with a basic package and upgrade as their requirements grow, maximizing revenue potential.
Salesforce’s focus on customer success and support ensures high satisfaction levels, which in turn supports upselling and cross-selling opportunities, further increasing revenue.
Who is responsible for AARRR metrics?
While the entire Product team contributes to the success of AARRR metrics, the following specific roles and departments often take the lead:
- Product Managers oversee the strategic implementation of AARRR metrics, ensuring alignment with overall product goals.
- Marketing Teams focus on acquisition and referral strategies to attract and expand the user base.
- UX Designers and Developers are key to improving activation and retention by enhancing the product’s usability and features.
- Sales and Customer Success Teams play a crucial role in maximizing revenue and encouraging referrals through positive user relationships.
Successfully implementing and managing your AARRR metrics requires collaboration across multiple roles and teams within your organization. Understanding and communicating who is responsible for each aspect of the AARRR framework can help ensure that everyone’s efforts are coordinated and your goals are achieved efficiently.
Common challenges and solutions when using AARRR metrics
While the AARRR framework is a robust model for driving your product growth and optimizing your user experience, implementing it isn’t without its challenges. Understanding these obstacles and knowing how to deal with them is vital for any Product Manager looking to get the best out of their AARRR metrics.
Let’s take a look at some common challenges and potential solutions.
Challenge: Data overload and analysis paralysis
With the wealth of data available, people can sometimes become overwhelmed, leading to analysis paralysis where no actionable decision is made.
Solution: Prioritize metrics that align closely with your current objectives and product stage. Use a dashboard that aggregates data in a digestible format, focusing on trends and changes over time rather than getting lost in the minutiae. Implement regular review cycles to assess progress and make decisions based on a balanced view of qualitative and quantitative data.
Challenge: Working out why the needle has moved
Attributing changes in metrics to specific actions or understanding the correlation between different metrics can be very complex, making it hard to identify what is driving success or failure.
Solution: Use controlled experiments to isolate variables and better understand their impact. Implement a consistent tagging and tracking system for marketing and product changes to correlate activities with shifts in metrics. Acknowledge the highly variable nature of user behavior, focusing on finding patterns and insights rather than definitive answers.
Challenge: Aligning cross-functional teams
The AARRR framework spans multiple aspects of a product and requires collaboration across many different departments, which can lead to alignment challenges.
Solution: Foster a shared understanding of the AARRR metrics and their importance through regular cross-functional meetings and reports. Establish clear ownership and responsibilities for each metric while encouraging open communication and collaboration. Use shared goals and even incentives to align efforts towards common objectives.
Challenge: Adapting AARRR strategies to different market segments
Products often serve diverse user segments, each with its own unique behaviors and needs, which can make it difficult to create a one-size-fits-all AARRR strategy.
Solution: Segment your user base and tailor AARRR strategies to each group. Analyze metrics by segment to identify distinct patterns and preferences, and adjust your tactics accordingly. This targeted approach allows for more personalized user experiences and effective optimization.
Challenge: Keeping up with changing user expectations and market dynamics
User preferences and market conditions constantly evolve, which can quickly render your previously successful strategies obsolete.
Solution: Cultivate a culture of continuous learning and flexibility within your team. Keep an eye on and regularly review external trends, competitor strategies, and user feedback to anticipate changes. Be prepared to pivot your strategies based on new information, testing new approaches to stay ahead of market shifts.
Challenge: Demonstrating ROI of AARRR initiatives
The Investments required to optimize your AARRR metrics may require significant resources, and stakeholders will expect to see a clear return on these efforts.
Solution: Establish clear benchmarks and goals for each AARRR initiative, including expected impacts on user behavior and revenue. Use dashboards and reports to track progress and outcomes, highlighting successes and learning from less effective efforts. Communicate your results in the context of overall business objectives to demonstrate the value of these initiatives.
Tools and resources for tracking AARRR metrics
Implementing and optimizing your AARRR metrics effectively will require the right set of tools and resources. These tools can help you to collect, analyze, and act upon the all data you need to make informed decisions.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the essential tools and resources for each stage of the AARRR framework, aimed at enhancing your Product Management strategy.
Acquisition tools
- Google Analytics: An indispensable tool for tracking website traffic and user behavior. It provides insights into how users find your site and what actions they take, helping you understand your most effective acquisition channels.
- SEMrush: A comprehensive SEO tool that helps improve your website’s visibility in search results, driving organic traffic. It offers keyword research, site audits, and competitor analysis.
- Facebook Ads Manager: For products utilizing social media marketing, Facebook Ads Manager allows you to create, manage, and optimize your ads across Facebook and Instagram, targeting specific demographics and interests.
Activation tools
- Mixpanel: Offers detailed insights into user actions within your product, allowing you to track how effectively new users are reaching your activation milestones.
- Hotjar: A tool for understanding user behavior through heatmaps, session recordings, and surveys. Hotjar can help identify usability issues that might be hindering user activation.
- Intercom: An AI-powered customer communication platform that can be used to engage with users through targeted messaging, in-app tutorials, and support, helping to improve activation rates.
Retention tools
- Amplitude: Specializes in product analytics for mobile and web, providing deep insights into user retention, segmentation, and lifecycle analysis.
- Customer.io: Enables targeted email and push notifications based on user behavior, which can be crucial for re-engaging users and improving retention.
Referral tools
- ReferralCandy: An e-commerce referral marketing tool that incentivizes existing customers to refer friends, driving new customer acquisition.
- Ambassador: Offers a robust platform for managing referral, affiliate, influencer, and partner marketing programs, making it easier to track and optimize referrals.
Revenue tools
- Stripe: An online payment processing platform that provides tools for managing subscriptions, invoicing, and revenue reporting.
- Baremetrics: Offers subscription analytics and insights for SaaS businesses, with features for tracking revenue, churn rate, and customer lifetime value (LTV).
- QuickBooks: An accounting software ideal for small to medium-sized businesses, helping track revenue, expenses, and profitability.
Cross-stage platforms
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool that can help combine and analyze data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of your AARRR metrics across stages.
- Looker Studio: Formally Google Data Studio, offers customizable reporting and dashboards, allowing you to aggregate data from different sources (like Google Analytics, AdWords, and CRM systems) to track AARRR metrics in one place.
- ProdPad: Acts as a comprehensive solution for managing product development across all AARRR stages. With its ability to integrate with various analytics tools, ProdPad provides a centralized platform for planning, tracking, and adjusting strategies based on AARRR metrics, ensuring that product decisions are data-driven and aligned with user needs and business objectives.
Choosing the right mix of tools and resources is crucial for effectively tracking and optimizing AARRR metrics. Each tool offers unique features that can help you to address specific challenges within the AARRR framework, from acquiring users to generating revenue.
By taking advantage of these tools, you can gain a deeper understanding of your users, streamline your Product Management processes, and drive growth.
Plus, by incorporating ProdPad into your toolset for managing AARRR metrics, you can centralize your product strategy, development, and optimization efforts. By using ProdPad alongside the specialized tools for each AARRR stage, you can ensure a cohesive approach, from understanding user behavior to driving growth and revenue.
