Product Management Best Practices: 8 Lean Methods Inspired by Industry Experts
Lean product management best practice is all about doing more with less, and creating more value for your customers with fewer resources. It’s a smart and agile approach to creating better products faster, inspired by Lean principles.
Adopting product management best practices can significantly streamline your processes. It’ll drive successful outcomes, maximizing the value you can get from minimal resources. Given that we’re all feeling the squeeze these days, this really can make a difference that might just save your backside.
This article will delve into Lean product management best practices, drawing examples from three product management experts: Janna Bastow, Christina Wodtke, and Teresa Torres. First, let’s look at what the product management best practices are and why they are important. Then we can take a deeper look at each one.
What are lean product management best practices?
Lean product management best practices are principles and techniques designed to create maximum value for customers while minimizing waste and optimizing resources. This approach borrows heavily from Lean principles originally developed in manufacturing and adapts them to the context of product management.
Key Lean product management best practices include:
- Focusing on customer-centric value creation: Creating value for the customer is key. Engage with customers regularly to understand their needs and feedback and continually improve your product based on these insights.
- Having a clear product vision: Define and communicate a clear product vision. This is a long-term goal that guides all product-related decisions and ensures everyone on the team is on the same page.
- Cultivating continuous discovery and experimentation: Validate your assumptions about your product and market through ongoing testing and learn from these experiments to improve your product. A culture of continuous discovery will keep you on top of market changes.
- Implementing the Build-Measure-Learn cycle: This Build-Measure-Learn involves building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), measuring its performance, learning from the results, and then iterating or pivoting based on these learnings.
- Using OKRs: Use Objective and Key Results (OKRs) to align goals and track progress within product teams. Regularly review these OKRs to ensure they remain relevant.
- Working on your user empathy: Develop a deep understanding of your customer base. Use user research techniques to understand their needs, motivations, and behaviors, and design your product to meet these needs.
- Establishing cross-functional collaboration: Promote collaboration and open communication between different teams involved in the product development process. This helps to ensure that everyone has a shared understanding of the product goals.
- Prioritizing ruthlessly: Prioritize the most impactful ideas that align with your product vision. Use a prioritization framework to make sure that you are working to release the right potential features.
Why are product management best practices important?
Product management best practices are pivotal to getting the most out of your team, and your product. They’ll provide you with the following benefits:
- Efficiency: Following best practices streamlines the product management process. It reduces time spent on non-value-adding activities and facilitating a smooth transition from ideation to execution.
- Customer Focus: Best practices, particularly in Lean product management, advocate for customer-centricity. By focusing on the customer’s needs, teams are more likely to develop products that truly resonate with their target audience.
- Risk Mitigation: Best practices help to mitigate risk. By implementing a structured, proven approach, product teams can avoid common pitfalls, validate assumptions early, and make informed decisions.
- Alignment and Communication: Best practices ensure alignment across the team. By defining a clear product vision, setting measurable objectives, and encouraging cross-functional collaboration, everyone involved in the product life cycle understands their role and the shared goals.
- Innovation: Product management best practices often involve fostering a culture of continuous learning and experimentation, which can drive innovation and enable the development of unique, competitive products.
- Quality and Consistency: Following best practices helps ensure consistency in product development processes, resulting in higher-quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Scalability: Best practices provide a solid foundation that can scale with the company as it grows. They offer a systematic approach to managing increasing product complexity and larger teams.
So, embracing product management best practices is an investment that can lead to improved product success, happier customers, and a healthier bottom line. Not too shabby, really.
Now, let’s look a little closer at the 8 product management best practices then, shall we?
Product Management Best Practices: The Lean Way
1. Establishing customer-centric value creation
Creating value for the customer is at the heart of Lean methodology. Janna Bastow, our CEO and co-founder of ProdPad, is a strong advocate for this, and she often extols the virtues of a customer-centric approach.
Lean product management leans heavily into this philosophy by engaging with customers regularly, extracting critical feedback, and continuously finessing the product offering based on this invaluable insight.
A great product management phrase is “NIHITO” – Nothing Important Happens In The Office. It’s best practice to look outside of your own organization to learn about your market and understand the problems you should be solving.
The best way to do this is by talking to your customers yourself in customer interviews or user testing, but you can also take advantage of the conversations your colleagues are having with their contacts, too. By bringing feedback into a single place, it’s easier to spot themes and identify the kinds of problems that rear their heads on a repeated basis.
ProdPad’s customer feedback tools and integration capabilities allow you to collect feedback from all the disparate places they’re circulating. It then allows you to link them to the ideas you have in your backlog to help understand the most valuable ones.
Even better, you’re able to engage your customers by involving them in testing the solutions they’ve asked for much earlier in the process, leading to better products and increased adoption rates.
For more ideas on how to gather customer feedback, check out our article on the 10 best ways to gather customer feedback online.
2. The guiding force of a great product vision
According to our CEO Janna, the bastion of successful product management is a well-articulated product vision. This long-term goal encapsulates the aspirations for your product and influences every decision related to product development. It fosters a shared understanding within the team and helps to steer the product strategy.
When was the last time you reviewed your product vision? Are you still aiming in the right direction? Your vision serves as the guiding star for all product-related decisions. It ensures that everyone on the team understands the ‘why’ behind what they’re doing and helps in maintaining the product’s strategic direction.
Just imagine the chaos that would ensue if you arranged to meet your friends for a night out without anyone picking a destination – it’s a vital bit of info, needed to make the whole thing work. Your vision is exactly that – it’s the information everyone needs so they know where they’re headed, and why.
If you find yourself needing any inspiration, try our product vision template. It’s designed to help you ask yourself the important questions, and create a vision that inspires your team.

Don’t forget, once you’ve defined your vision, you need to make sure everyone can see it. ProdPad’s product and portfolio canvases help you keep the vision front and center, right where everyone needs it. By aligning everyone around the long-term goal, you’ll reduce misunderstandings and help your team stay on track.
3. Advocating for a culture of continuous discovery
Teresa Torres, a leading product discovery coach, promotes a culture of continuous discovery and experimentation. In Lean product management, it is crucial to validate your assumptions and hypotheses about your product and market through continuous testing.
Torres drives home the importance of continuous discovery, and integrating what you learn from these experiments into your product. It encourages curiosity, which helps to foster a culture of innovation. You should keep experimenting with different features and aspects of your product, learn from these experiments, and incorporate the learnings into your product.
Hungry for more? We’ve written before about the value of continuous discovery in agile product management, and we’ve also had the pleasure of Teresa joining us on a webinar which you can watch on-demand here.
4. Embrace the Build-Measure-Learn cycle
The Build-Measure-Learn cycle forms the backbone of Lean product management. It encourages teams to build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), measure how it performs, learn from the results, and then iterate or pivot based on the learnings.
Christina Wodtke, author and lecturer at Stanford University, maintains that every step of this process is essential. Skipping one or rushing through another may lead to the development of a product that is not match up with market needs or customer expectations.
5. The power of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
Christina also endorses implementing OKRs to align your goals and keep track of your product teams’ progress. If your product vision defines the destination, your OKRs help you to set the route.
Your objectives highlight what needs to be achieved, while the key results you monitor serve as tangible indicators of success. Regular reviews ensure your OKRs remain relevant and continue to drive the team and product forward.
Product management best practice suggests your objectives must be qualitative – what are you going to improve? Maybe it’s adoption, usability, scalability, or similar. Key results should be measurable – how will you know you’ve made improvements? What metrics can you check which will show you’ve made a positive impact?
Write up your OKRs and make sure they’re documented somewhere everyone can see them. You’ll find it much easier to see if what you’re doing is actually working as you execute against your roadmap.
If you need a bit more guidance on how to go about it, we’ve written about OKRs here. If you need a way to manage them, ProdPad gives you a place to document your OKRs and tie them directly to the plans on your Lean roadmap, so they’re always considered in your plans.
6. Understanding users through empathy
As highlighted by Teresa Torres, empathy is the bridge that connects product managers to their users and fuels a deep and nuanced understanding. It’s one of the things that makes a long-lived and successful product. To create a product that truly resonates with users and stands out in the market, it’s crucial to gain insights into their needs, motivations, and behaviors, their challenges and pain points.
Cultivating empathy goes beyond simply recognizing user needs; it involves immersing yourself in the user’s world, and understanding their experiences on a deeper level. This empathetic approach can enable product managers to perceive subtle nuances, discover unspoken needs, and design solutions that fit seamlessly into the user’s life.
A range of user research techniques can be employed to cultivate empathy. Torres points to the importance of conducting interviews, surveys, and usability tests to gather user insights. You can gain different perspectives for using each of the following tools in combination:
- Interviews provide a direct line of communication with users. They allow product managers to delve into users’ thoughts and feelings, uncover their motivations, and understand the context in which they interact with the product.
- Surveys enable product managers to gather data from a large user base. While they may not offer the same depth of understanding as interviews, they can provide valuable quantitative data and highlight common themes or trends among users.
- Usability tests offer a first-hand look at how users interact with a product. By observing users as they navigate the product, product managers can identify any points of friction or confusion and refine the user experience accordingly.
Theresa underscores that empathy-building is not a one-time activity. User needs and behaviors evolve over time, and you need to be continuously researching to stay attuned to these changes. As the product evolves and grows, new user segments may emerge, and ongoing user research ensures that the product remains relevant and valuable for all its users.
Theresa suggests that empathy should not be the responsibility of product managers alone. Cultivating a user-centric mindset across the entire team—from design and development to marketing and sales—can lead to more comprehensive user insights and better product decisions.
By sharing user research findings and involving the team in user research activities, everyone can gain a deeper understanding of your users and work together to create a product that truly meets their needs.
Cultivating empathy is fundamental product management best practice that can drive product success. Through continuous user research, product managers can build a deep understanding of their users, design solutions that truly resonate with them, and ultimately, create products that deliver value and delight users.
7. Cross-functional collaboration for coherent product goals
A productive environment thrives when team members can freely express their insights and be an active part of the product development process. It boosts morale and ensures a holistic approach to problem-solving. Product managers are well-positioned when they embrace and empower their team’s diverse perspectives.
Having a centralized idea backlog (or “opportunity backlog” as Silicon Valley Product Group’s founder Marty Cagan calls it) gives everyone the chance to contribute their thoughts and get visibility into where they sit in the ideation process.
This shared platform brings double the benefits. It provides product managers with a rich reservoir of ideas from their teams and allows shared decision-making, increasing the likelihood of launching market-fit solutions by mitigating risks in decision-making.
Platforms like ProdPad exemplify these product management best practices by fostering collaboration among all internal stakeholders. Free Reviewer licenses mean you don’t need to worry about how much that extra help will cost.
Plus, having an efficient platform facilitates documentation of discussions and decisions, providing an easy reference for future review. Even your Slack and email chats can be captured along the way, making it much easier to backtrack and remind yourself how you reached a conclusion
8. Prioritization: the key to efficient execution
Janna points out the necessity for ruthless prioritization in product management. The pool of good ideas always exceeds the bandwidth for implementation. Identifying and focusing on the most impactful ideas that align with your product vision becomes crucial. There are many different prioritization frameworks that you can use to ensure that you are focusing on the right things.
At ProdPad we advocate using a Now-Next-Later roadmap – it’s not a static document, but a dynamic blueprint that mirrors the market problems you aim to solve, providing room for your teams to explore and experiment.
Customers resonate deeply with a problem-focused roadmap. It’s an assurance that their voices are heard and understood. Moreover, it offers them an opportunity to propose potential solutions, contributing to your product strategy without causing strategic upheaval.
Reflect on your existing roadmap. Does it target high-priority issues? Have you brainstormed potential solutions? Are the objectives clearly linked? Does it offer room to pivot as required? Is it comprehensible for all? Above all, does it provide the context behind your chosen focus areas?
If you’re answering ‘no’ to any of these questions, it might be an indicator that you’d benefit from pivoting towards a Lean roadmap. This approach aligns well with product management best practices, providing a more efficient and effective way to manage product strategy.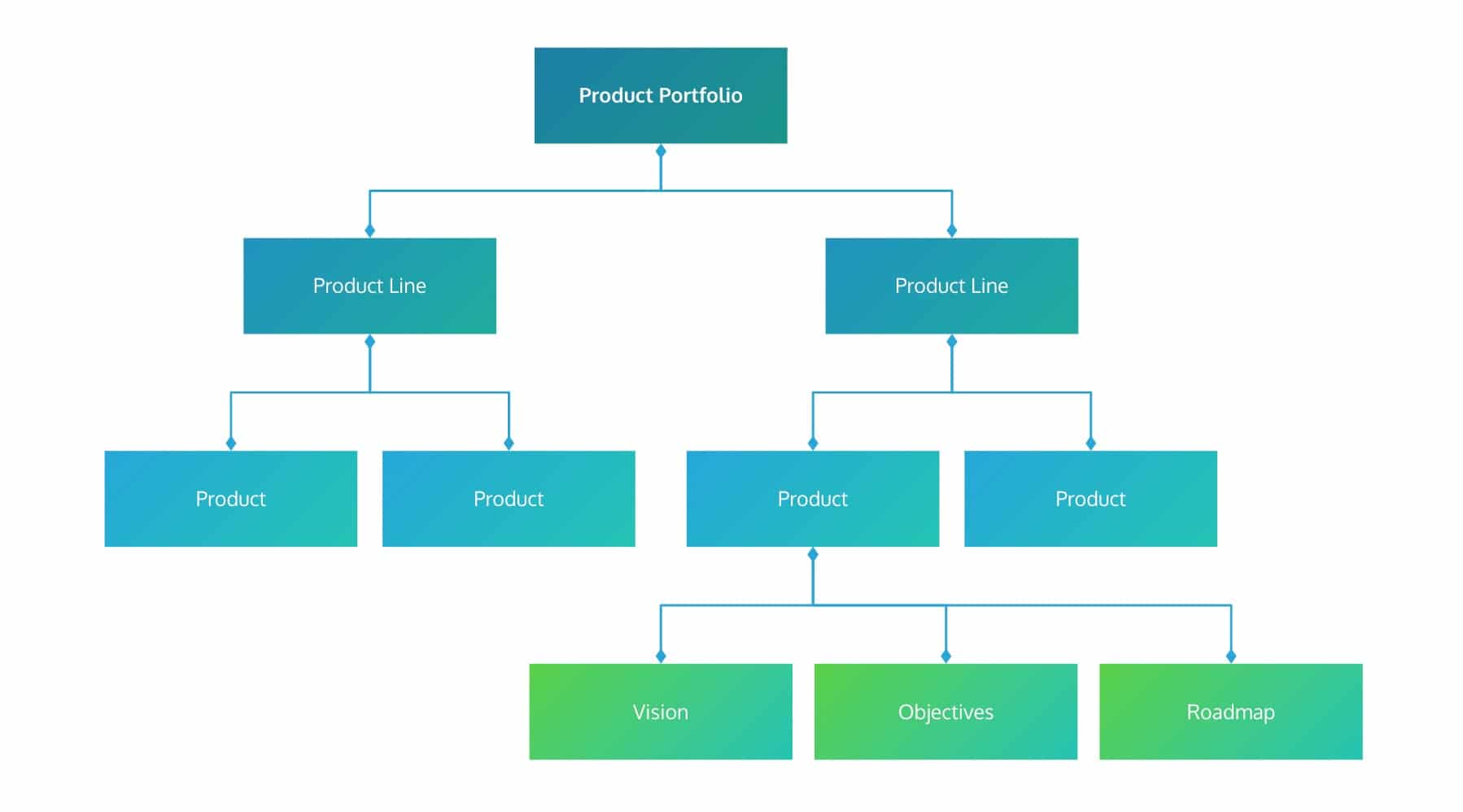
Bring product management best practices together with a Lean Now-Next-Later roadmap
The cornerstone of a well-coordinated team is a clear vision and set objectives, establishing a shared understanding of the product’s future and the journey to get there. This strategic plan is often embodied in a product roadmap.
Lean roadmapping holds a crucial role in communicating the product strategy. It offers flexibility, encourages innovation, and crucially, it focuses on the issues that need addressing.
Are you ready to take off? Start your free trial in ProdPad and get everyone ready for the journey ahead. 🚀

