Affinity Grouping
What is Affinity Grouping?
Affinity grouping, also known as affinity diagramming, affinity mapping, or affinity estimation, is a prioritization technique in which a group organizes a wide range of ideas and data into natural relationships. It is essentially a workshop session that can help with identifying the common themes and patterns that emerge from user feedback, customer satisfaction surveys, and employee suggestions.
The process involves using sticky notes or index cards to capture individual ideas, user stories, or potential features, and then categorizing them into groups that share a similar theme. This helps you to visualize the larger picture, and identify potential actionable goals for the team or organization.
The affinity process typically takes place with a large, cross-functional group, with a leader organizing the session. Agile development teams often use it to prioritize user outcomes and inform the product roadmap. It can help to identify common themes and potential risks across the development process.
Overall, affinity grouping can help you to make informed decisions based on qualitative data. It’s a flexible and adaptable technique that is useful in a variety of settings, from product development to design improvement and more. It can enhance collaboration and help you to identify actionable insights.
How does Affinity Grouping work?
The affinity grouping process involves multiple steps (see the next section below), beginning with a brainstorming session. Team members generate a list of ideas, user stories, or potential features related to a specific problem or opportunity.
You then write each idea on a separate sticky note or index card and then categorize them into a thematic cluster based on their similarities to other ideas.
After categorizing the ideas, the team can then begin to analyze the data and identify common themes and potential actionable goals. The end result is a comprehensive affinity diagram that provides a useful visual representation of the team’s collective insights and recommendations.
This prioritization method is most effective when done in large groups with multiple stakeholders involved. This is so that you can generate more ideas and ensure you have covered considerations from different perspectives.
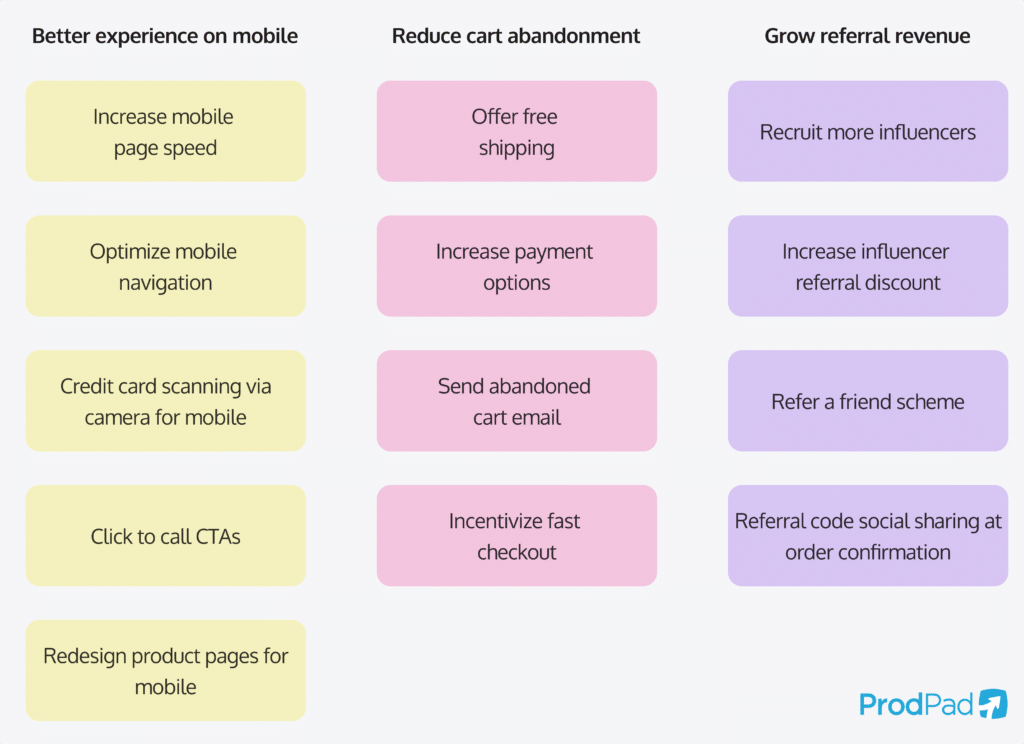
How do you run an Affinity Grouping session?
Before you begin, it’s important to establish guidelines and ground rules. This helps to ensure that everyone feels comfortable and confident in sharing their ideas. You’ll also need to be careful to make sure that all of your team members have an equal opportunity to share their ideas and that you have a fair and transparent voting process.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to run an Affinity Grouping session:
1. Define the objective
Start by defining the objective of the session. What problem are you trying to solve or what ideas are you looking to generate? Make sure that everyone on the team is clear about the objective.
2. Brainstorm ideas
Give the team members a set amount of time to brainstorm ideas related to the objective. Encourage everyone to contribute their ideas and write them down on sticky notes or index cards – no judgment, all ideas welcome.
3. Group similar ideas
Once a sufficient number of ideas have been generated, group them together based on their relatedness or similarity. This can be done by reviewing each idea and identifying common themes or categories.
4. Name the groups
Once you have grouped similar ideas together, give each group a name that reflects the common theme or pattern. This will make it easier to refer to the groups later.
5. Discuss the groups
Once all the ideas have been grouped and named, discuss each group in turn. Ask team members to elaborate on the ideas within each group and explore any potential solutions or opportunities.
6. Prioritize ideas
After discussing all the groups, prioritize the ideas based on their impact, feasibility, and alignment with the product vision and goals.

7. Define the next steps
Finally, define the next steps based on the prioritized ideas. Assign tasks to team members and create an action plan for implementing the ideas.
It’s important to note that affinity grouping is not a one-size-fits-all process. You may need to customize it to fit the specific needs of your team or organization. However, with its simple process and collaborative experience, affinity grouping can be a powerful tool for agile teams, product owners, product managers, and other stakeholders to prioritize user outcomes and inform the design improvement process.
By encouraging creativity, collaboration, and open communication, affinity grouping can help team members to work together more effectively and produce better outcomes for their customers.
It’s a simple process that helps to democratize the decision-making process and encourages team members to think creatively and collaboratively.
How can you use Affinity Grouping?
Affinity grouping is a versatile and effective technique that you can use in a variety of settings and situations. It is particularly useful for product teams, development teams, and design teams who are looking to improve their customer satisfaction, design processes, and product outcomes.
It can be particularly helpful in the development of product roadmaps and in managing backlogs. By clustering ideas and user stories into thematic groups, teams can gain a deeper understanding of the natural relationships and common themes. This allows them to identify the most important features and improvements that will have the greatest impact on user outcomes and customer satisfaction.
You can also use it in brainstorming sessions to generate new ideas and solutions to complex problems. Product managers can then easily identify the most popular ideas and prioritize those when deciding which ones to pursue. Your teams can then focus on key areas of improvement, ensuring that their efforts are aligned with your customers’ needs.
Another application of affinity grouping is in the design process. You can use it to identify potential design improvements, such as new features, user interface enhancements, and other design changes that will improve usability and overall customer satisfaction. Teams can identify areas where additional research or design work is needed and ensure that the design process remains focused on the most important goals and outcomes.
You can also use affinity grouping to address a wide range of challenges associated with the development and design process. For example, you can use it to identify potential risks in new product development projects or to evaluate the effectiveness of existing design processes and workflows.
What are the benefits of Affinity Grouping?
There are several ways that using the affinity grouping method can be useful to you and your team, including:
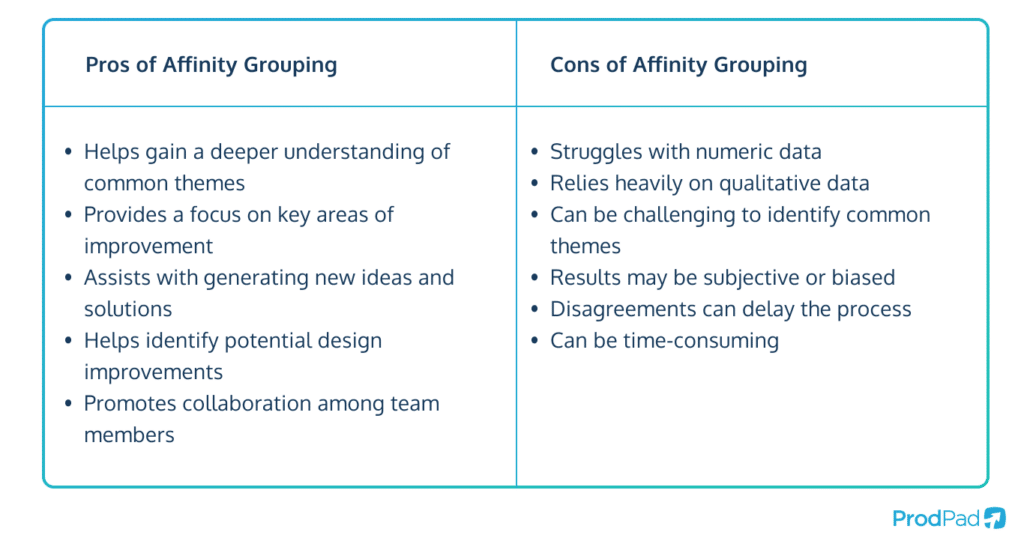
- Helping teams gain a deeper understanding of the natural relationships and common themes in their qualitative data.
- Enabling you to focus on key areas of improvement and ensuring your teams’ efforts are aligned with customer needs.
- Assisting with generating new ideas and solutions.
- Helping to identify potential design improvements that will improve usability and overall customer satisfaction.
- Promoting collaboration among team members.
What are the downsides of Affinity Grouping
While it’s often a beneficial process, affinity grouping isn’t always ideal and does have some notable drawbacks. You may find that:
- It may not work well with numeric data or data that cannot be easily categorized into thematic clusters.
- It relies heavily on qualitative (non-numeric) data and may not capture important numeric insights.
- It can be challenging to identify natural relationships and common themes within the data, which can lead to inaccurate or incomplete grouping.
- It may be subjective and influenced by personal biases.
- It may result in disagreements among team members on how the data should be grouped, which can delay the process and stifle collaboration.
- It can be time-consuming, especially if there is a wide range of ideas or feedback to be clustered.
When should you try using Affinity Grouping?
Affinity grouping is an effective technique for organizing and making sense of qualitative data, especially when it comes to identifying themes and relationships.
It can be helpful if you are planning, or already in the middle of, a brainstorming session. If you have a wide range of ideas from different sources, try turning it into an affinity grouping activity. This can help the group to narrow down the important ideas and determine the next steps to take.
It is often useful during product development, as using this technique will help your team to group user outcomes and stories into actionable goals and design improvements that align with your product roadmap.
Affinity grouping may also be beneficial during the design process, especially when trying to improve customer satisfaction. By identifying themes and commonalities in user feedback, a product manager or owner can make the necessary design tweaks to improve the user experience.
You can also use it when conducting employee feedback surveys to gauge employee satisfaction. The process of affinity grouping can help to identify common themes and potential areas of improvement for the company culture or work environment.
Affinity grouping is a versatile prioritization tool that you can use in a variety of scenarios. It is a simple and effective way to organize qualitative data and identify key insights that will drive actionable results.